ntIn any triangle ABC, prove the following: a(cosB.cosC+cosA) = b(cosC.cosA+cosB) = c(cosA.cosB+cosC)n
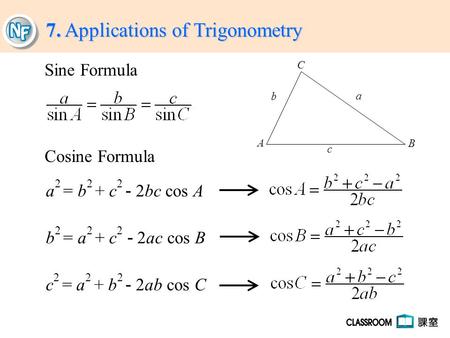
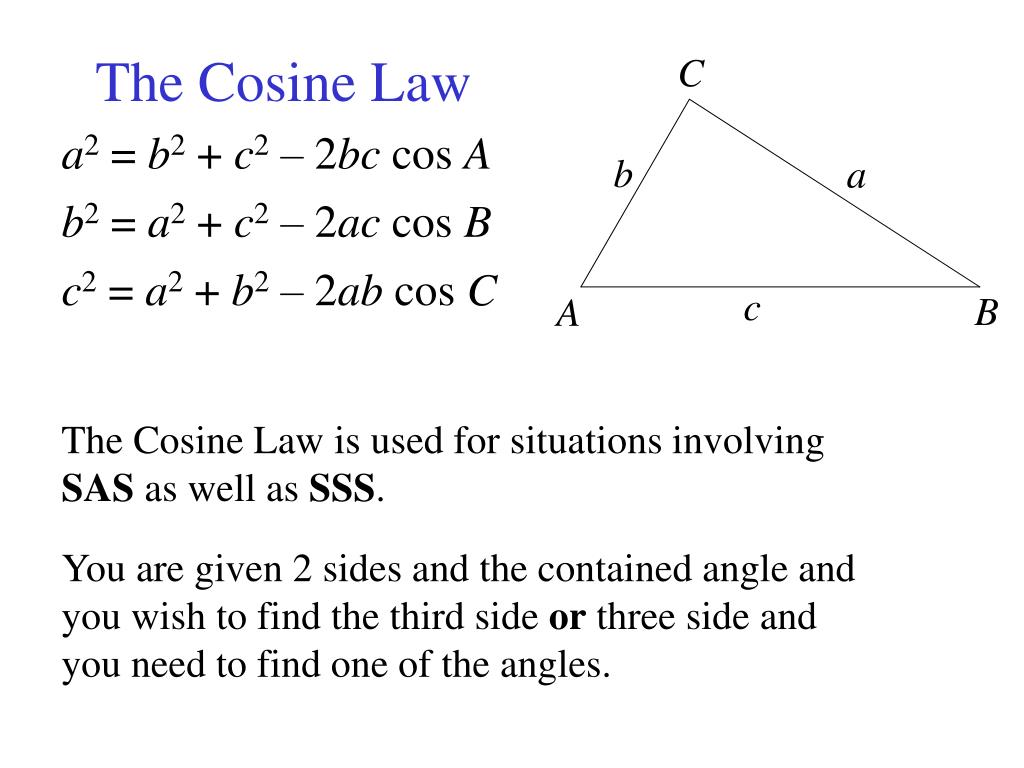
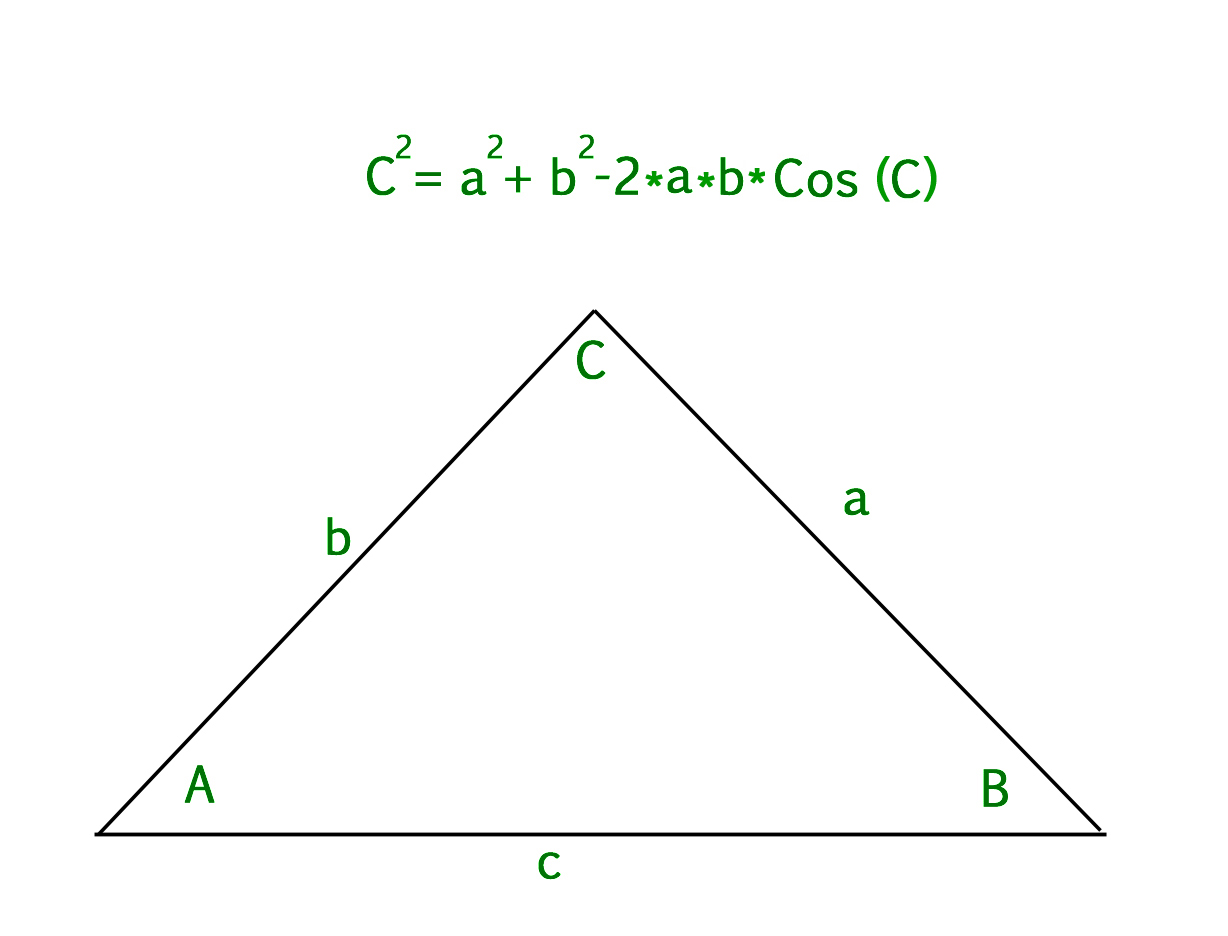
The Cosine Law The Cosine Law is used for situations involving SAS as well as SSS. You are given 2 sides and the contained angle and you wish to find the. -
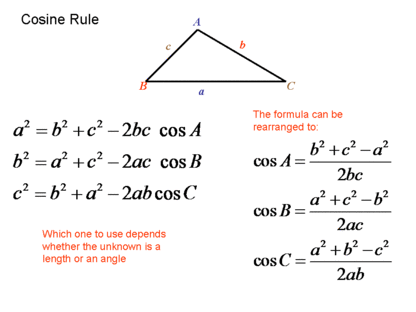
A triangle has sides A, B, and C. Sides A and B are of lengths 5 and 8, respectively, and the angle between A and B is (11pi)/12 . What is the
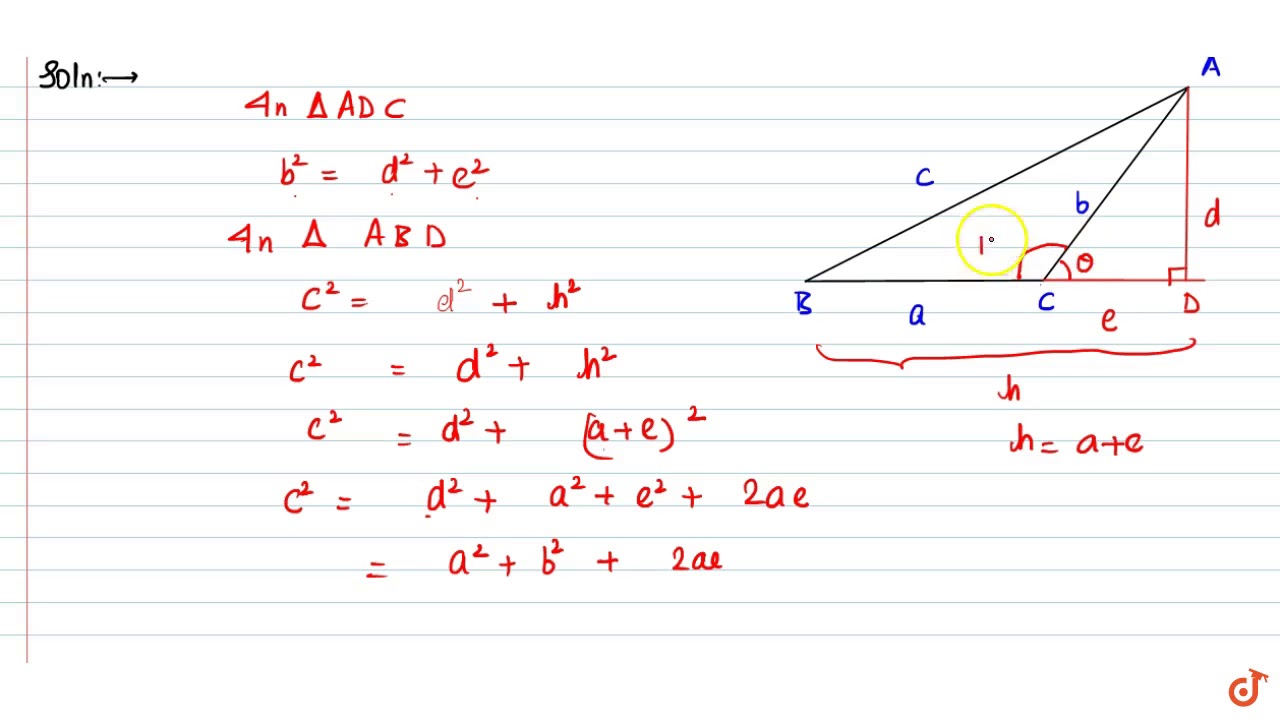
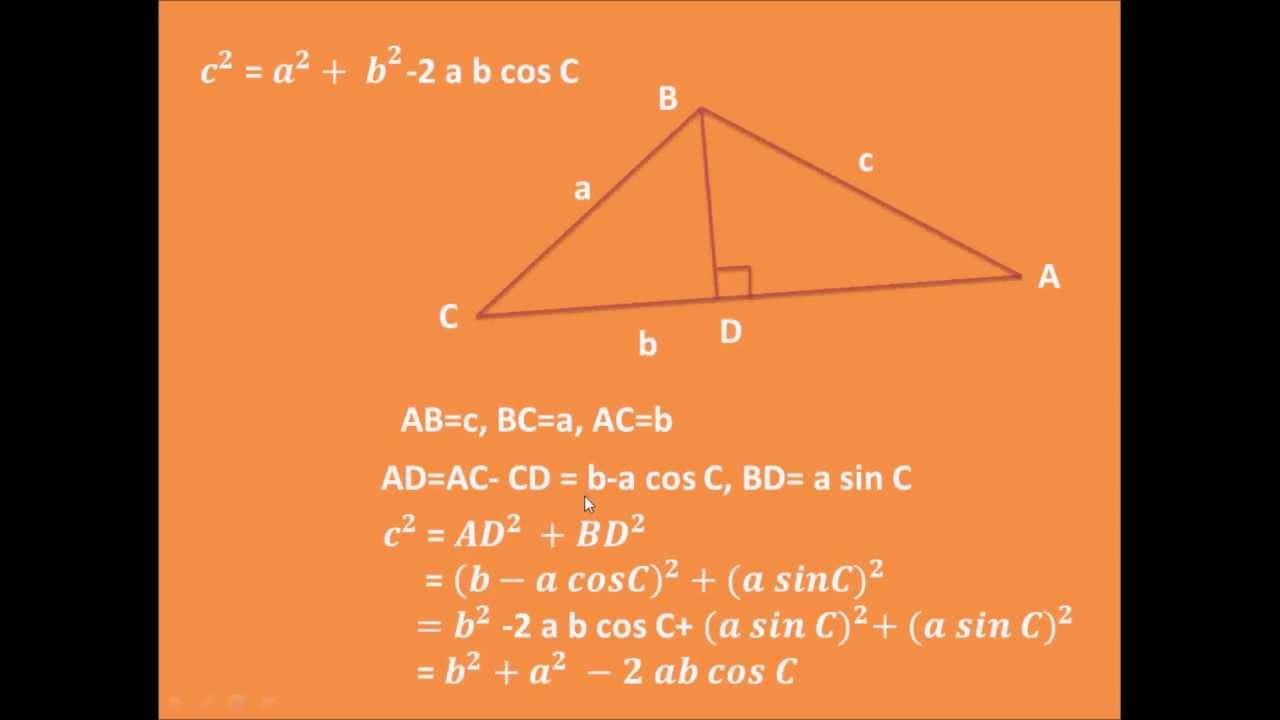
In the law of cosines, why do we add -2ab*cos(C)? My understanding is that this law is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem, and comes from (a+b) ²=a²+b²+2ab and the cos(C) accounts


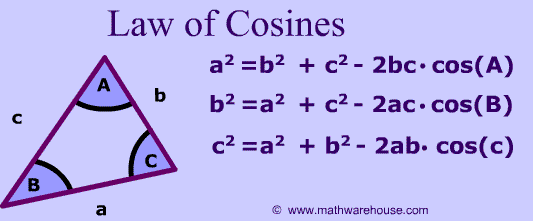
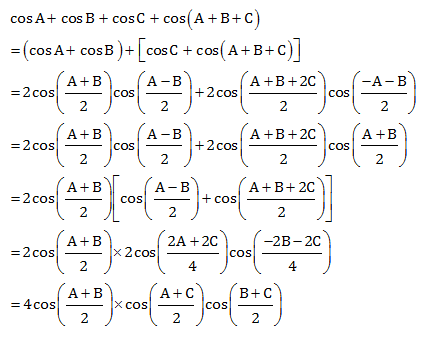








}&line2=\mathrm{Solution:\:}\sec(c))